- English
- 中文
What is a thyristor?
Time: 2022-10-27 14:55:09
Author: Bruce Chen
From: LJ-MD
Click:
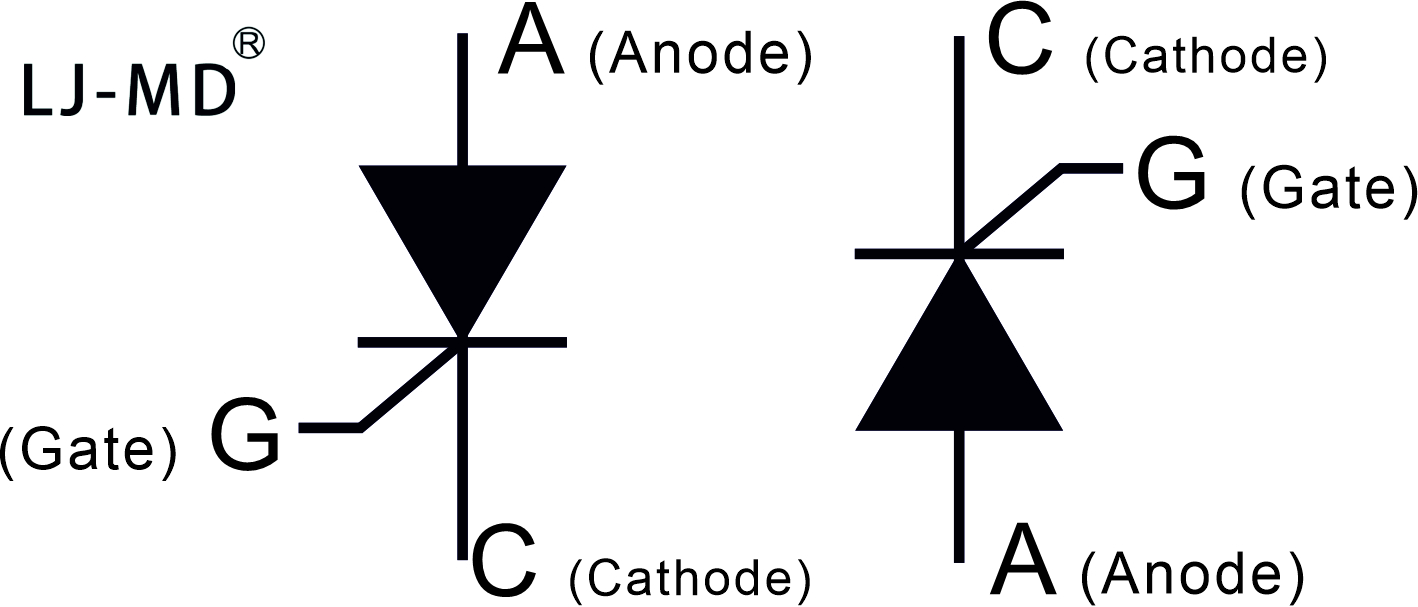
Unlike the junction diode, which is a two-layer (P-N) semiconductor device, or the common bipolar transistor, which is a three-layer (P-N-P or N-P-N) switching device, a thyristor is a four-layer (P-N-P-N) semiconductor device with three PN junctions connected in series and through represented the symbols shown in the figure.
Like a diode, a thyristor is a unidirectional device; H. it only conducts current in one direction, but unlike a diode, a thyristor can operate as an open switch or as a rectifying diode, depending on how the thyristor gate is triggered. In other words, thyristors can only work in switching mode and cannot be used for amplification.
Silicon controlled rectifier SCR is one of several power semiconductor devices, in addition to triac (transistor alternating current), triac (diode alternating current) and UJT (unijunction transistor), all of which can act like very fast transistors. Solid state AC switches work as well to control large AC voltages and currents. So for electronics students, these are very handy solid state devices for controlling AC motors, lights and phase control.
A thyristor is a three-terminal device, identified as: "anode", "cathode" and "gate", consisting of three PN junctions that can be switched "ON" and "OFF" extremely quickly, or an "on" Variable amount of time within a half-cycle to deliver a selected amount of power to the load The operation of a thyristor is best explained by assuming that it consists of two transistors connected back-to-back as a pair of complementary regenerative switches, such as shown in the figure.